Difference between revisions of "Spark"
| (6 intermediate revisions by 4 users not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| − | [[Category:Software]][[Category: | + | [[Category:Software]][[Category:Utility]] |
{|<!--CONFIGURATION: REQUIRED--> | {|<!--CONFIGURATION: REQUIRED--> | ||
|{{#vardefine:app|spark}} | |{{#vardefine:app|spark}} | ||
| Line 24: | Line 24: | ||
Run <code>module spider {{#var:app}}</code> to find out what environment modules are available for this application. | Run <code>module spider {{#var:app}}</code> to find out what environment modules are available for this application. | ||
==System Variables== | ==System Variables== | ||
| − | * HPC_{{ | + | * HPC_{{uc:{{#var:app}}}}_DIR - installation directory |
| − | * HPC_{{ | + | * HPC_{{uc:{{#var:app}}}}_BIN - executable directory |
| − | * HPC_{{ | + | * HPC_{{uc:{{#var:app}}}}_SLURM - SLURM job script examples |
* SPARK_HOME - examples directory | * SPARK_HOME - examples directory | ||
==Running Spark on HiperGator== | ==Running Spark on HiperGator== | ||
| − | To run your Spark jobs on HiperGator, | + | To run your Spark jobs on HiperGator, two separate steps are required: |
| + | |||
| + | # Create a Spark cluster on HiperGator via SLURM. This section "Spark Cluster on HiPerGator" below shows a simple example how to create a Spark cluster on HiperGator. | ||
| + | # Submit your job to your Spark cluster. You can do this either interactively at the command line ("Spark Interactive Job" section below) or by submitting a a batch job ("Spark Batch Job" section below) | ||
| + | |||
| + | For details about running Spark jobs on HiPerGator, please refer to [https://help.rc.ufl.edu/doc/Spark_Workshop Spark Workshop]. For Spark parameters used in this section, please refer to [https://spark.apache.org/ Spark's homepage]. | ||
===Spark cluster on HiperGator=== | ===Spark cluster on HiperGator=== | ||
| Line 38: | Line 43: | ||
It is assumed that spark-local-cluster.sh is the file name of the SLURM job script for one-worker node Spark cluster in this section. | It is assumed that spark-local-cluster.sh is the file name of the SLURM job script for one-worker node Spark cluster in this section. | ||
Set SLURM parameters for Spark cluster. spark-local-cluster.sh is available on "Spark_Job_Scripts" page below. | Set SLURM parameters for Spark cluster. spark-local-cluster.sh is available on "Spark_Job_Scripts" page below. | ||
| − | < | + | <pre> |
#!/bin/bash | #!/bin/bash | ||
#filename: spark-local-cluster.sh | #filename: spark-local-cluster.sh | ||
| Line 50: | Line 55: | ||
module load spark | module load spark | ||
| − | |||
| − | Set Spark parameters for Spark cluster | + | ## Set Spark parameters for Spark cluster |
| − | |||
export SPARK_LOCAL_DIRS=$HOME/spark/tmp | export SPARK_LOCAL_DIRS=$HOME/spark/tmp | ||
export SPARK_WORKER_DIR=$SPARK_LOCAL_DIRS | export SPARK_WORKER_DIR=$SPARK_LOCAL_DIRS | ||
| Line 61: | Line 64: | ||
export SPARK_NO_DAEMONIZE=true | export SPARK_NO_DAEMONIZE=true | ||
export SPARK_LOG_DIR=$SPARK_LOCAL_DIRS | export SPARK_LOG_DIR=$SPARK_LOCAL_DIRS | ||
| − | + | ||
mkdir -p $SPARK_LOCAL_DIRS | mkdir -p $SPARK_LOCAL_DIRS | ||
| − | |||
| − | Set Spark Master and Workers | + | ##Set Spark Master and Workers |
| − | |||
MASTER_HOST=$(scontrol show hostname $SLURM_NODELIST | head -n 1) | MASTER_HOST=$(scontrol show hostname $SLURM_NODELIST | head -n 1) | ||
export SPARK_MASTER_NODE=$(host $MASTER_HOST | head -1 | cut -d ' ' -f 4) | export SPARK_MASTER_NODE=$(host $MASTER_HOST | head -1 | cut -d ' ' -f 4) | ||
export MAX_SLAVES=$(expr $SLURM_JOB_NUM_NODES - 1) | export MAX_SLAVES=$(expr $SLURM_JOB_NUM_NODES - 1) | ||
| − | # for starting spark master | + | |
| + | ## for starting spark master | ||
$SPARK_HOME/sbin/start-master.sh & | $SPARK_HOME/sbin/start-master.sh & | ||
| − | # use spark defaults for worker resources (all mem -1 GB, all cores) since using exclusive | + | |
| − | #for starting spark worker | + | ## use spark defaults for worker resources (all mem -1 GB, all cores) since using exclusive |
| + | ## for starting spark worker | ||
$SPARK_HOME/sbin/start-slave.sh spark://$SPARK_MASTER_NODE:$SPARK_MASTER_PORT | $SPARK_HOME/sbin/start-slave.sh spark://$SPARK_MASTER_NODE:$SPARK_MASTER_PORT | ||
| − | </ | + | </pre> |
Submit the SLURM job script to HiperGator | Submit the SLURM job script to HiperGator | ||
| Line 174: | Line 177: | ||
<!--Job Scripts--> | <!--Job Scripts--> | ||
{{#if: {{#var: job}}|==Job Script Examples== | {{#if: {{#var: job}}|==Job Script Examples== | ||
| − | + | <div class="mw-collapsible mw-collapsed" style="width:70%; padding: 5px; border: 1px solid gray;"> | |
| + | ''Expand this section to view spark-local-cluster.sh'' | ||
| + | <div class="mw-collapsible-content" style="padding: 5px;"> | ||
| + | <source lang=bash> | ||
| + | #!/bin/bash | ||
| + | #filename: spark-local-cluster.sh | ||
| + | |||
| + | #SBATCH --job-name=spark_cluster | ||
| + | #SBATCH --nodes=1 # nodes allocated to the job | ||
| + | #SBATCH --cpus-per-task=16 # the number of CPUs allocated per task | ||
| + | #SBATCH --exclusive # not sharing of allocated nodes with other running jobs | ||
| + | #SBATCH --time=03:00:00 | ||
| + | #SBATCH --output=spark_cluster.log | ||
| + | #SBATCH --error=spark_cluster.err | ||
| + | |||
| + | ###SBATCH --ntasks= # tasks to be created for the job | ||
| + | ###SBATCH --ntasks-per-core= # max number of tasks per allocated core | ||
| + | ###SBATCH --ntasks-per-node= # max number of tasks per allocated node | ||
| + | ###SBATCH --mail-type=END,FAIL | ||
| + | ###SBATCH --mail-user=<yourID>@ufl.edu | ||
| + | |||
| + | module load spark | ||
| + | ### Set Spark variables | ||
| + | export SPARK_LOCAL_DIRS=$HOME/spark/tmp | ||
| + | export SPARK_WORKER_DIR=$SPARK_LOCAL_DIRS | ||
| + | export SPARK_WORKER_CORES=$SLURM_CPUS_PER_TASK | ||
| + | export SPARK_MASTER_PORT=7077 | ||
| + | export SPARK_MASTER_WEBUI_PORT=8080 | ||
| + | export SPARK_NO_DAEMONIZE=true | ||
| + | export SPARK_LOG_DIR=$SPARK_LOCAL_DIRS | ||
| + | #export SPARK_CONF_DIR=$SPARK_LOCAL_DIRS | ||
| + | mkdir -p $SPARK_LOCAL_DIRS | ||
| + | |||
| + | MASTER_HOST=$(scontrol show hostname $SLURM_NODELIST | head -n 1) | ||
| + | export SPARK_MASTER_NODE=$(host $MASTER_HOST | head -1 | cut -d ' ' -f 4) | ||
| + | export MAX_SLAVES=$(expr $SLURM_JOB_NUM_NODES - 1) | ||
| + | |||
| + | # start master | ||
| + | $SPARK_HOME/sbin/start-master.sh & | ||
| + | |||
| + | # start workers | ||
| + | # use spark defaults for worker resources (all mem -1 GB, all cores) since using exclusive | ||
| + | |||
| + | $SPARK_HOME/sbin/start-slave.sh spark://$SPARK_MASTER_NODE:$SPARK_MASTER_PORT | ||
| + | </source> | ||
| + | </div> | ||
| + | </div> | ||
| + | <div class="mw-collapsible mw-collapsed" style="width:70%; padding: 5px; border: 1px solid gray;"> | ||
| + | ''Expand this section to view pi_with_pythonstartup.py'' | ||
| + | <div class="mw-collapsible-content" style="padding: 5px;"> | ||
| + | <source lang=python> | ||
| + | from operator import add | ||
| + | from random import random | ||
| + | |||
| + | partitions =10 | ||
| + | n = 100000 * partitions | ||
| + | |||
| + | def f(_): | ||
| + | x = random() * 2 - 1 | ||
| + | y = random() * 2 - 1 | ||
| + | return 1 if x ** 2 + y ** 2 <= 1 else 0 | ||
| + | |||
| + | count = sc.parallelize(range(1, n + 1), partitions).map(f).reduce(add) | ||
| + | print("Pi is roughly %f" % (4.0 * count / n)) | ||
| + | </source> | ||
| + | </div> | ||
| + | </div> | ||
|}} | |}} | ||
<!--Policy--> | <!--Policy--> | ||
Latest revision as of 22:01, 15 December 2022
Description
Apache Spark is a fast and general-purpose cluster computing system. It provides high-level APIs in Java, Scala, Python and R, and an optimized engine that supports general execution graphs. It also supports a rich set of higher-level tools including Spark SQL for SQL and structured data processing, MLlib for machine learning, GraphX for graph processing, and Spark Streaming.
Environment Modules
Run module spider spark to find out what environment modules are available for this application.
System Variables
- HPC_SPARK_DIR - installation directory
- HPC_SPARK_BIN - executable directory
- HPC_SPARK_SLURM - SLURM job script examples
- SPARK_HOME - examples directory
Running Spark on HiperGator
To run your Spark jobs on HiperGator, two separate steps are required:
- Create a Spark cluster on HiperGator via SLURM. This section "Spark Cluster on HiPerGator" below shows a simple example how to create a Spark cluster on HiperGator.
- Submit your job to your Spark cluster. You can do this either interactively at the command line ("Spark Interactive Job" section below) or by submitting a a batch job ("Spark Batch Job" section below)
For details about running Spark jobs on HiPerGator, please refer to Spark Workshop. For Spark parameters used in this section, please refer to Spark's homepage.
Spark cluster on HiperGator
Expand this section to view instructions for creating a spark cluster in HiperGator.
It is assumed that spark-local-cluster.sh is the file name of the SLURM job script for one-worker node Spark cluster in this section. Set SLURM parameters for Spark cluster. spark-local-cluster.sh is available on "Spark_Job_Scripts" page below.
#!/bin/bash #filename: spark-local-cluster.sh #SBATCH --job-name=spark_cluster #SBATCH --nodes=1 # nodes allocated to the job #SBATCH --cpus-per-task=16 # the number of CPUs allocated per task #SBATCH --exclusive # not sharing of allocated nodes with other running jobs #SBATCH --time=03:00:00 #SBATCH --output=spark_cluster.log #SBATCH --error=spark_cluster.err module load spark ## Set Spark parameters for Spark cluster export SPARK_LOCAL_DIRS=$HOME/spark/tmp export SPARK_WORKER_DIR=$SPARK_LOCAL_DIRS export SPARK_WORKER_CORES=$SLURM_CPUS_PER_TASK export SPARK_MASTER_PORT=7077 export SPARK_MASTER_WEBUI_PORT=8080 export SPARK_NO_DAEMONIZE=true export SPARK_LOG_DIR=$SPARK_LOCAL_DIRS mkdir -p $SPARK_LOCAL_DIRS ##Set Spark Master and Workers MASTER_HOST=$(scontrol show hostname $SLURM_NODELIST | head -n 1) export SPARK_MASTER_NODE=$(host $MASTER_HOST | head -1 | cut -d ' ' -f 4) export MAX_SLAVES=$(expr $SLURM_JOB_NUM_NODES - 1) ## for starting spark master $SPARK_HOME/sbin/start-master.sh & ## use spark defaults for worker resources (all mem -1 GB, all cores) since using exclusive ## for starting spark worker $SPARK_HOME/sbin/start-slave.sh spark://$SPARK_MASTER_NODE:$SPARK_MASTER_PORT
Submit the SLURM job script to HiperGator
sbatch spark-local-cluster.sh
Check the Spark master launched.
grep "Starting Spark master" spark_cluster.err
This grep command above should end up with information like
18/03/13 14:53:23 INFO Master: Starting Spark master at spark://c29a-s42.ufhpc:7077
Check the Spark worker launched.
grep "Starting Spark worker" spark_cluster.err
This grep command above should end up with information like
18/03/13 14:53:24 INFO Worker: Starting Spark worker 172.16.194.59:42418 with 16 cores, 124.3 GB RAM
Spark interactive job
Expand this section to view instructions for starting preset applications without a job script.
Spark supports interactive job submission through the interactive shells.
- Spark interactive shell in Scalar (spark-shell)
First, load spark module in the terminal where you want to submit a spark job.
module load spark
Get the location of the Spark master to connect to it through the interactive shell
SPARK_MASTER=$(grep "Starting Spark master" *.err | cut -d " " -f 9)
Connect to the master using the Spark interactive shell in scalar
spark-shell --master $SPARK_MASTER
- Spark interactive shell in Python (pyspark)
Load spark module in the terminal where you want to submit a spark job.
module load spark
Get the location of the Spark master to connect to it through the interactive shell
SPARK_MASTER=$(grep "Starting Spark master" *.err | cut -d " " -f 9)
Connect to the master using the Spark interactive shell in scalar
pyspark --master $SPARK_MASTER
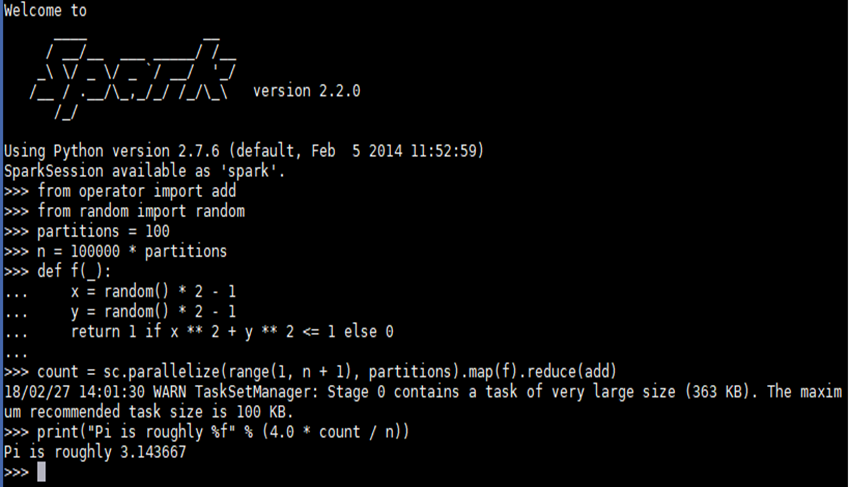
- Example - PI estimation via pyspark
SPARK_MASTER=$(grep "Starting Spark master" *.err | cut -d " " -f 9) pyspark --master $SPARK_MASTER
- Example - Pi estimation from file with pyspark
As of Spark 2.0., Spark interactive shell in python does not load python files to run python application. Instead, “PYTHONSTARTUP”, a python environmental variable can be used to run python script with pyspark, which executes the python script before an interactive shell starts.
SPARK_MASTER=$(grep "Starting Spark master" *.err | cut -d " " -f 9) PYTHONSTARTUP=pi_with_pythonstartup.py pyspark --master $SPARK_MASTER
pi_with_pythonstartup.py script is avaialble on "Spark_Job_Scripts" page below.
Spark batch job
Expand this section to view instructions for starting preset applications without a job script.
Spark supports batch job submission through spark-submit which provides unified interface for Spark jobs
$SPARK_HOME/bin/spark-submit \
--class <main-class> --master <master-url> \
--deploy-mode <deploy-mode> --conf <key>=<value> \
... # other options <application-jar> [application-arguments]
--class: The entry point for your application (e.g. org.apache.spark.examples.SparkPi) --master: The master URL for the cluster (e.g. spark://123.45.67.890:7077) --deploy-mode: Whether to deploy your driver on the worker nodes (cluster) or locally as an external client (client) (default: client) --conf: Arbitrary Spark configuration property in key=value format. For values that contain spaces wrap “key=value” in quotes (as shown). <application-jar>: Path to a bundled jar including your application and all dependencies. The URL must be globally visible inside of your cluster, for instance, an hdfs:// path or a file:// path that is present on all nodes. <application-arguments>: Arguments passed to the main method of your main class, if any
For further details about spark-submit, refer to https://spark.apache.org/docs/2.2.0/submitting-applications.html.
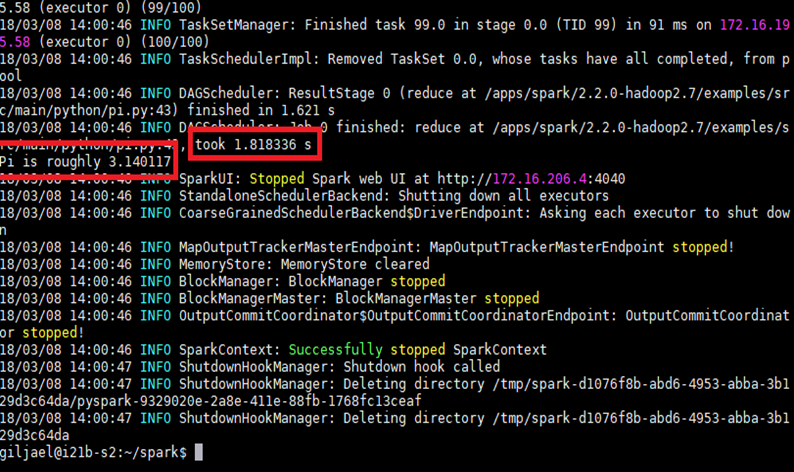
- Example - Pi estimation via Spark-submit
SPARK_MASTER=$(grep "Starting Spark master" *.err | cut -d " " -f 9) spark-submit --master $SPARK_MASTER $SPARK_HOME/examples/src/main/python/pi.py 10
Job Script Examples
Expand this section to view spark-local-cluster.sh
#!/bin/bash
#filename: spark-local-cluster.sh
#SBATCH --job-name=spark_cluster
#SBATCH --nodes=1 # nodes allocated to the job
#SBATCH --cpus-per-task=16 # the number of CPUs allocated per task
#SBATCH --exclusive # not sharing of allocated nodes with other running jobs
#SBATCH --time=03:00:00
#SBATCH --output=spark_cluster.log
#SBATCH --error=spark_cluster.err
###SBATCH --ntasks= # tasks to be created for the job
###SBATCH --ntasks-per-core= # max number of tasks per allocated core
###SBATCH --ntasks-per-node= # max number of tasks per allocated node
###SBATCH --mail-type=END,FAIL
###SBATCH --mail-user=<yourID>@ufl.edu
module load spark
### Set Spark variables
export SPARK_LOCAL_DIRS=$HOME/spark/tmp
export SPARK_WORKER_DIR=$SPARK_LOCAL_DIRS
export SPARK_WORKER_CORES=$SLURM_CPUS_PER_TASK
export SPARK_MASTER_PORT=7077
export SPARK_MASTER_WEBUI_PORT=8080
export SPARK_NO_DAEMONIZE=true
export SPARK_LOG_DIR=$SPARK_LOCAL_DIRS
#export SPARK_CONF_DIR=$SPARK_LOCAL_DIRS
mkdir -p $SPARK_LOCAL_DIRS
MASTER_HOST=$(scontrol show hostname $SLURM_NODELIST | head -n 1)
export SPARK_MASTER_NODE=$(host $MASTER_HOST | head -1 | cut -d ' ' -f 4)
export MAX_SLAVES=$(expr $SLURM_JOB_NUM_NODES - 1)
# start master
$SPARK_HOME/sbin/start-master.sh &
# start workers
# use spark defaults for worker resources (all mem -1 GB, all cores) since using exclusive
$SPARK_HOME/sbin/start-slave.sh spark://$SPARK_MASTER_NODE:$SPARK_MASTER_PORT
Expand this section to view pi_with_pythonstartup.py
from operator import add
from random import random
partitions =10
n = 100000 * partitions
def f(_):
x = random() * 2 - 1
y = random() * 2 - 1
return 1 if x ** 2 + y ** 2 <= 1 else 0
count = sc.parallelize(range(1, n + 1), partitions).map(f).reduce(add)
print("Pi is roughly %f" % (4.0 * count / n))