Getting Started
Welcome to UF Research Computing! This page is intended to help new users understand and use UFRC resources. Be sure to check out our training schedule if you'd like help getting started in person!
From Zero to HiPerGator
There are many approaches and resources a researcher can use to analyze their data. Some analyses can be performed on a laptop or a desktop in the lab. Some analyses that rely on proprietary technologies can be done at least partially with resources and applications provided by the vendor. Some researchers are able to 'game' the cloud spot instance market to find relatively cheap resources to perform their analyses on commercial computational resources and are able to install, manage, and use all applications and workflows they need on their own. However, study after study shows that local HPC resources subsidized by the institution still provide the best cost and level of service to academic researchers. Our own cloud vs. HPC cost comparison supports this notion. At the University of Florida researchers arguably have access to the best of both worlds - low cost resources and top-notch systems, application, and research facilitation support.
Once analyses move beyond what an individual computer can handle and a UF research group decides to seek additional computational resources the process usually starts from the following steps:
- If a face-to-face discussion about the group's needs is needed one of the group's members or the group's sponsor (usually a UF faculty member) can meet one of the UF Research Computing Facilitators or submit a support request to start the conversation.
- Once a decision is made to try HiPerGator group members should submit HiPerGator account requests at which point a group and an account for the group's Faculty or Staff sponsor will be created.
- Group's sponsor (usually a UF faculty member) should request a trial allocation on HiPerGator.
- Group members can now use HiPerGator for 3 months. They should submit support requests if a new application or help with an error is needed or there is a question about applications, workflows, scheduler usage or anything else related to HiPerGator. Note that there are over a thousand installed applications on HiPerGator already. See below on how to use environment modules to search for and enable them.
- Once the trial is over and the group has a rough idea of what computational and storage resources it needs the group's sponsor should submit a purchase request to invest into the resources the group needs. Some groups may have access to shared departmental allocations in which case group members should submit support requests to be added to the appropriate account. Some examples of departments with shared allocations include the Genetics Institute, Emerging Pathogens Institute, Statistics Department, Biostatistics Department, Center for Compressible Multiphase Turbulence (CCMT), Cognitive Aging and Memory Clinical Translational Research Program (CAMCTRP), Center for Molecular Magnetic Quantum Materials, Physics Department, and Plant Pathology Department. In addition, several research groups working on collaborative projects have shared allocations accessible to members of those projects.
- Note: a computational allocation is mandatory! No analyses can be run on HiPerGator without a computational allocation.
Creating an Account
To be able to do anything on HiPerGator you need a UF Research Computing account. To create an account with UF Research Computing, you must read the UFRC Account Policy. After you have reviewed the policy, go to our website to submit an account request. You will have to tell us the name of the Principal Investigator (PI) who sponsors the access of the group. Once the PI approves your access to their allocation your account will be created; the username and password will be the same as your GatorLink username and password.
If you are a new Principal Investigator you will need to indicate this on the request form, so that we can create a new group for you. Please note that to do useful work, your group will have to invest into computational resources, or you will have to join a departmental group with a shared allocation.
Connecting to HiPerGator
To work on HiPerGator you will have to connect to it from your local computer either via SSH (terminal session) or via one of the web/application interfaces we provide such as Galaxy or Matlab (for Matlab distributed computing toolbox pilot project we are testing).
Note about using this guide: for any given command, <username> should be replaced with the UFRC username (same as your GatorLink username).
For example, if you are referencing the command ssh <username>@hpg.rc.ufl.edu and your Gatorlink username is smith, you would use the command:
ssh smith@hpg.rc.ufl.edu
Connecting from Windows
Expand this section to view instructions for logging in with Windows.
Since Microsoft Windows does not come with a built-in SSH client, you must download a client from the web.
UFRC recommends using PuTTY or MobaXterm.
PuTTY
- Download PuTTY to your local machine and start the program .
- Connect to hpg.rc.ufl.edu.
- At the login prompt, enter your username (this should be the same as your GatorLink username)
- Enter your password when prompted. You are now connected and ready to work!
MobaXterm
- Download MobaXterm to your local machine and start the program.
- Click "Start local terminal"
- Open a terminal and run
ssh <username>@hpg.rc.ufl.edu - Enter your password when prompted. You are now connected and ready to work!
Connecting from Linux
Expand this section to view instructions for logging in with Linux/Unix.
Open a terminal and run
ssh <username>@hpg.rc.ufl.edu
Enter your password when the prompt appears. You are now connected and ready to work!
Connecting from MacOS X
Expand this section to view instructions for logging in with OS X.
For OS X users, connection instructions are very similar to those for Linux users.
Terminal, the terminal emulation application for OS X, is located in the folder Applications/Utilities.
Start the Terminal application and run
ssh <username>@hpg.rc.ufl.edu
Enter your password when the prompt appears. You are now connected and ready to work!
Transferring Data
If you need to transfer datasets to or from HiPerGator and your local computer or another external location you have to pick the appropriate transfer mechanism.
Samba
Samba service, also known as a 'network share' or 'mapped drive' provides you with an ability to connect to some HiPerGator filesystems as locally mapped drives (or mount points on Linux or MacOS X). Once you connected to a share this mechanism provides you with a file transfer option that allows you to use your client computer's native file manager to access and manage your files. Samba works best for moving smaller files, like job scripts, to and from the system. You must be connected to the UF network (either on-campus or through the VPN) to connect to Samba shares.
- See the page on accessing Samba for setup information specific to your computer's operating system.
SFTP
SFTP, or secure file transfer, works well for small to mediaum data transfers and is appropriate for both small and large data files.
If you would like to use a Graphical User Interface ecure file transfer client we recommend:
After you have chosen and downloaded a client, configure the client to connect to hpg.rc.ufl.edu, specifying port number 22. Use your username and password to log in.
Rsync
If you prefer to use the command-line or to get maximum efficiency from your data transfers Rsync, which is an incremental file transfer utility that minimizes network usage, is a good choice. It does so by transmitting only the differences between local and remote files rather than transmitting complete files every time a sync is run as SFTP does. Rsync is best used for tasks like synchronizing files stored across multiple subdirectories, or updating large data sets. It works well both for small and large files. See the Rsync page for instructions on using rsync.
Globus
Globus is a high-performance mechanism for file transfer. Globus works especially well for transferring large files or data sets
- See the Globus page for setup and configuration information.
Automounted Paths
Note: NFS-based storage on our systems are typically automounted, which means they are dynamically mounted only when users are actually accessing them. For example if you have an invested folder as /orange/smith, to access it you will have to specifically type in the full path of "/orange/smith" to be able to see the contents and access them. Directly browsing /orange will not show the smith sub-folder unless someone else is using it coincidentally. Automounted folders are pretty common on the systems, they include /orange, /bio, /rlts and even /home etc.
Editing your files
Several methods exist for editing your files on the cluster.
Native Editors
- vi - The visual editor (vi) is the traditional Unix editor; however, it is not necessarily the most intuitive editor. View a tutorial for using vi
- emacs - Emacs is a much heavier duty editor, but again has the problem of having commands that are non-intuitive. View a tutorial for using emacs
- pico - While pico is not installed on the system, nano is installed, and is a pico work-a-like.
- nano - Nano has a good bit of on-screen help to make it easier to use.
External Editors
You can also use your favorite file editor on your local machine, and then transfer the files to the cluster afterward. A caveat to this is that files created on Windows machines usually contain unprintable characters, which may be misinterpreted by Linux command interpreters (shells). If this happens, there is a utility called dos2unix that you can use to convert the text file from DOS/Windows formatting to Linux formatting.
Using installed software
The full list of software available for use can be viewed on the Installed Software page. Access to installed software is provided through Environment Modules.
The following command can be used to browse the full list of available modules, along with short descriptions of the applications they make available:
module spider
To load a module, use the following command:
module load <module_name>
For more information on loading modules to access software, view the page on the basic usage of environment modules.
There are some useful commands and utilities in a 'ufrc' environment module in addition to installed applications.
Doing Interactive Testing or Development
You don't always have to use the SLURM scheduler. When all you need is a quick shell session to run a command or two, write and/or test a job script, or compile some code use SLURM Dev Sessions.
Running Graphical Programs
It is possible to run programs that use a graphical user interface (GUI) on the system. However, doing so requires an installation of and configuration of additional software on the client computer.
Please see the GUI Programs page for information on running graphical user interface applications at UFRC.
Scheduling jobs using SLURM
UFRC uses the Simple Linux Utility for Resource Management, or SLURM, to allocate resources and schedule jobs. Users can create SLURM job scripts to submit jobs to the system. These scripts can, and should, be modified in order to control several aspects of your job, like resource allocation, email notifications, or an output destination.
- See the Annotated SLURM Script for a walk-through of the basic components of a SLURM job script
- See the Sample SLURM Scripts for several SLURM job script examples
To submit a job script from one of login nodes via hpg.rc.ufl.edu, use the following command:
$ sbatch <your_job_script>
To check the status of submitted jobs, use the following command:
$ squeue -u <username>
View SLURM_Commands for more useful SLURM commands.
Managing Cores and Memory
The amount of resources within an investment is calculated in NCU (Normalized Computing Units), which correspond to 1 CPU core and about 3.5GB of memory for each NCU. NCU resources in an allocation can be consumed either by requesting more CPU cores while staying below 3.5GB of memory per core or by requesting more memory than the NCU ratio per core. System will automatically calculate the usage according to the 1 CPU core to 3.5GB memory ratio. This ratio is determined by the form factor of the compute nodes on HiPerGator. Most nodes have 32 or 64 cores and 128 or 256 GB of RAM. The bigmem nodes and the newer Skylake nodes have a higher ratio of 16 GB/core and 6 GB/core, respectively. The majority of HiPerGator nodes, old and new, have the same ratio of about 4 GB or RAM per core, which, after accounting of the operating systems and system services, leaves about 3.5 GB usable for jobs. See Available_Node_Features for the exact data on resources available on all types of nodes on HiPerGator.
You must specify both the number of cores and the amount of RAM needed in the job script for SLURM with the pmem or mem-mer-cpu option. Otherwise, the job will be assigned the default 600mb of memory.
For example, if you need to run with 4 cores and pmem=6GB of RAM, then SLURM will provide 4 cores subtract 4 NCUs from the allocation in the QOS you are using investment because the job RAM limit is below the 3.5 GB/core.
If, for example, you need to use 1 core and pmem=42GB to have more memory available to the application you are running then SLURM will allocate 42GB of memory on the node which it assigns to your job and will subtract 12 NCUs out of the QOS allocation even though you are using only one core, because you are using the amount of memory associated with 12 NCUs.
If you need more than 128 GB or RAM, you can only run on the older nodes, which have 256 GB of RAM, or on the bigmem nodes, which have up to 1.5 TB of RAM.
See Account and QOS limits under SLURM for an extensive explanation of QOS and SLURM account use.
Getting help
If you are having problems using the UFRC system, please let our staff know by submitting a support request.
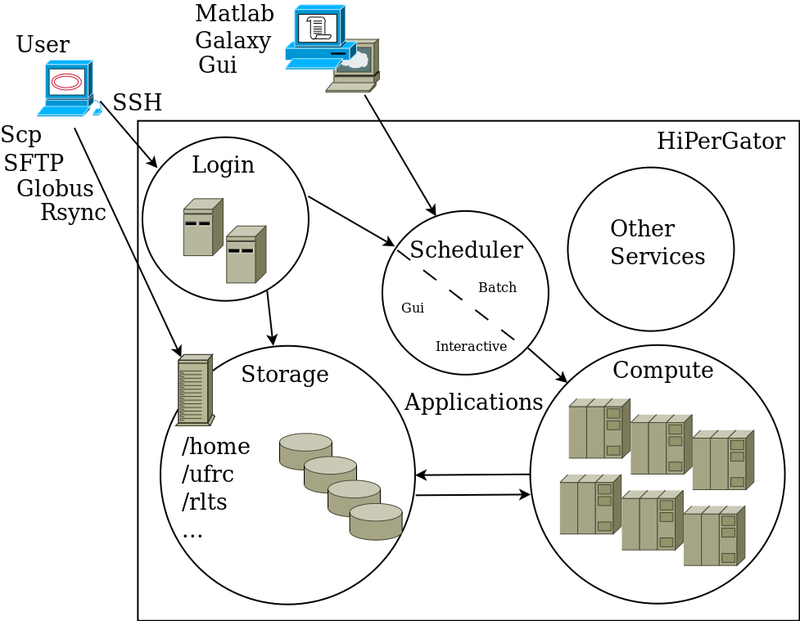
Visual Overview
The diagram below shown a high-level overview of HiPerGator use. We will go over each part in sections below